Internet Explorer And High CPU Usage
Internet Explorer often shows high CPU usage. It also shows a high RAM consumption. The reason for Internet Explorer and high CPU usage is the fact that Internet Explorer is made up of several components that use software rendering to display websites on your display. Here is a small experiment. Close all open Internet Explorer windows and re-open just one IE window. Press CTRL + ALT + DEL or right click on the Windows Taskbar to open Windows Task Manager. You can see more than one instance of iexplore.exe running. This is due to the fact the Windows recognizes some components of the Internet Explorer as a different process and hence, displays them separately. However, this alone is not responsible for Internet Explorer and high CPU usage. You can perform the same experiment for other browsers – Firefox and Chrome - and see that they too show up as two or more processes in the Windows Task Manager.
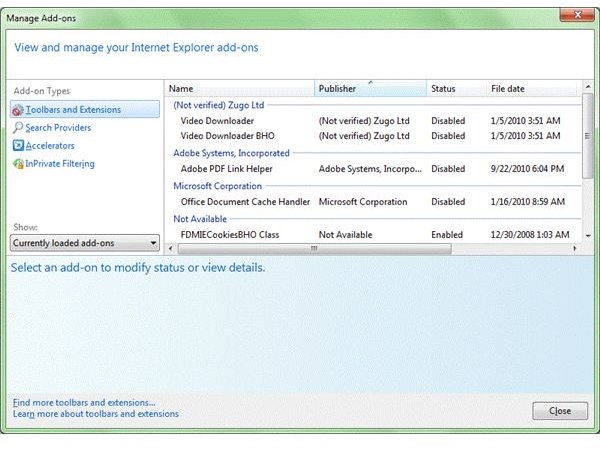
To decrease high CPU usage, Internet Explorer 9 employs hardware acceleration instead of software. Chrome employs the technique partially. Among other factors that contribute to the high CPU usage are the IE add-ons. By default, IE carries plenty of add-ons – whether or not you use them. Microsoft changed this practice in IE9, thereby reducing the load on CPU. If you open the add-on management dialog (Tools menu -> Manage Add-ons) in any version of IE prior to IE9, you will notice a hoard of add-ons like Discuss, Research, Translate, etc. Most of the end users are people who use the browser only for viewing websites and they do not need such kind of add-ons. Other than the default add-ons, almost every program that you install on your machine, also installs an IE helper (add-on), making the Internet Explorer, a heavy resource consuming browser.
Effect of Toolbars and Tabs
Another major problem is using too many toolbars. Some programs try to add Ask toolbar even without your knowledge. People already use different toolbars (Google, Bing, and more) with IE to manage bookmarks and for spell-checking etc. Fortunately, with the release of IE9 beta, most of these problems seem to be gone as the latest browser alerts you about the add-ons and components. When something adds a plugin to your IE9, the browser provides you with an alert so that you can see the load time of each component. This helps you in managing add-ons and toolbars for optimal performance of the browser. For more details, please read my article on IE9 compared to IE8.
Opening too many tabs also forces high load on CPU. I have seen people using each new webpage in a new tab, making it up to 15 tabs in the same IE window. This tendency leads to high resource consumption and more importantly, regular freezing and crashing of all the tabs in IE.
Thus, the major factors that force high CPU usage in Internet Explorer are: external components of Internet Explorer (the ones not in IE shell); add-ons; accelerators; and toolbars. Website designs also contribute to high CPU usage in Internet Explorer. Complex websites with plenty of scripts and animations force IE to use computer resources heavily so that it can render the website properly. Some examples are ebay, Yahoo, GoDaddy, etc.
Having discussed the main reasons for Internet Explorer and high CPU usage, let us now see how to customize the browser to reduce resource consumption. Please turn to the next page for the information.
Tips to Reduce CPU Usage in Internet Explorer
Unfortunately, we cannot do anything with the IE shell components that may prove heavy on computer resources. But we sure can customize almost all other factors to reduce the high CPU us
age in Internet Explorer.
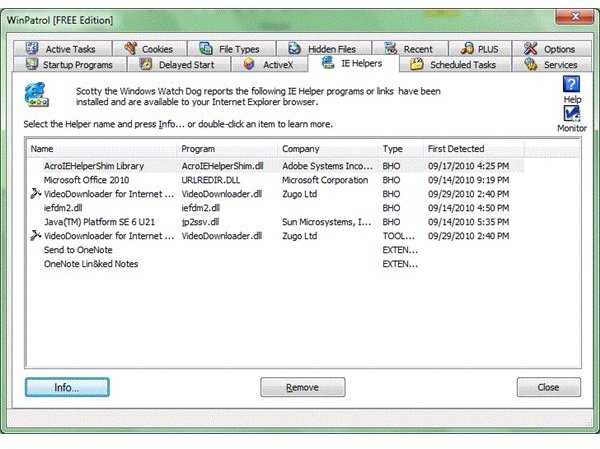
First of all, I would suggest you to install something that can track changes to your copy of IE. I use WinPatrol, a program that tracks changes to all my programs and to my computer (see image). It alerts me if any program installs a new IE add-on. You can always open Winpatrol -> IE Helpers to see what all is included in the IE. You can turn off or remove the unwanted add-ons using the program. It also checks for startup programs so you can also use it to reduce the startup speed of your computer.
You can also check the current add-ons, accelerators, search engines, etc by opening the Manage Add-ons dialog box. Click on the Tools menu (tools icon in Internet Explorer 9) and select Manage Add-ons. The Dialog box presents you with a list of add-ons, accelerators, and other IE Helpers that are currently packed into the browser. For IE9, you can also see the load time so it becomes easy for you to decide which ones to keep. For IE8 and previous versions, most of the add-ons are not really useful for you unless you are a website developer. Some such add-ons are Research, Discuss, Translate, etc. You can always disable them to reduce CPU usage in Internet Explorer. Similarly, check out the accelerators – email, blog, and more. You certainly won’t need such accelerators. Disabling them will not only reduce the resource consumption, it will also speed up your copy of Internet Explorer.
Note: If you are not sure about an IE Helper (addon), you can google it to see what it is and if you really need it on the browser.
Managing Toolbars and Tabs to Deal with High CPU Usage in Internet Explorer
Toolbars can also be managed using the same dialog box. It does not matter how many toolbars you installed for the IE. What matters is how many are active. You can disable the toolbars to increase the speed of your browser while also saving on the resources. While you may remove unwanted toolbars using the Manage Add-ons -> Toolbars, you can also use Control Panel -> Add/Remove Programs (Windows XP) or Programs and Features (Windows 7). If you think you can use a toolbar in future, you can just right click on an empty area on the address bar and disable it. For instance I have a video download toolbar, which I seldom use. But I do not wish to remove it either - as it helps me download videos from Facebook and similar sites. I keep it disabled until I need to download any video. This is another method to reduce CPU usage without having to remove all the toolbars.
Finally, the number of tabs open in a single window of Internet Explorer also decides the CPU usage. I do not recommend using more than four to five tabs in a single window. If you need to open more websites, open another instance (window) of IE instead of creating a new tab. This is good for both decreasing the CPU usage as well as making your browser less prone to freezes and crashes.
This was a primer on Internet Explorer and high CPU usage. If you have anything to add, please feel free to use our comments section.